|
×
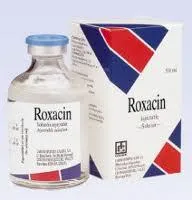
Енрофлоксацин (ROXACIN) 10% 250мл Callier
ROXACIN 100mg/ml Fluoroquinolone antibiotic PHARMACEUTICAL FORM: Injectable solution COMPOSITION: Enrofloxacin 100mg/ml INDICATIONS: Treatment of bacterial infections caused by strains susceptible to enrofloxacin. Cattle and Pigs: Respiratory infections caused by Pasteurella spp. or Mycoplasma spp. Alimentary tract infections caused by E. coli Cattle: Treatment of local signs (inflammation, milk qualit y and yield) associated with peracute/acute mastitis in lactating dairy cattle caused by E. coli DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ROUTE: Cattle and pigs: Respiratory and alimentary infections and secondary bacterial infections: Administer 2,5mg of enrofloxacin/kg bw/day for 3 day s (equivalent to 2.5 ml of ROXACIN/100 kg bw). This rate may be doubled to 5 mg/kg bw (equival ent to 5 ml of ROXACIN/100kg bw) for 5 days in case of complicated respiratory disease. Administration route: cattle – SC, pigs – IM. Not more than 2.5 ml should be administered at any one intramuscular injection site. Not more than 10 ml should be administered at any one subcutaneous injection site Cattle: E. coli mastitis: Administer by slow intravenous injection 5mg of enrofloxacin/kg bw (equivalent to 5ml of ROXACIN/100kg bw) daily for 2 days. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Do not use for prophylaxis. Do not use when resista nce/cross resistance to (Fluoro)quinolones is known to occur. Do not use in the case of known hyp ersensitivity to fluoroquinolones or to any of the excipients. WITHDRAWAL PERIOD: Cattle: Pigs: Subcutaneous use Intravenous use Intramuscular Use Meat and offal: 10 days Meat and offal: 4 days Meat and offal: 10 days Milk: 84 hours (7 milkings) Milk: 72 hours (6 milki ngs) PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES: Enrofloxacin is bactericidal in action with a conce ntration dependent activity against a wide range of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria and mycopl asmas. The mechanism of action of the quinolones relies upon their ability to inhibit bac terial DNA gyrase, an enzyme responsible for controlling the supercoiling of bacterial DNA durin g replication. The fluoroquinolones also possess activity against bacteria in the stationary phase b y an alteration of the permeability of the outer membrane phospholipid cell wall ROXACIN 100mg/ml Fluoroquinolone antibiotic PHARMACEUTICAL FORM: Injectable solution COMPOSITION: Enrofloxacin 100mg/ml INDICATIONS: Treatment of bacterial infections caused by strains susceptible to enrofloxacin. Cattle and Pigs: Respiratory infections caused by Pasteurella spp. or Mycoplasma spp. Alimentary tract infections caused by E. coli Cattle: Treatment of local signs (inflammation, milk qualit y and yield) associated with peracute/acute mastitis in lactating dairy cattle caused by E. coli DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION ROUTE: Cattle and pigs: Respiratory and alimentary infections and secondary bacterial infections: Administer 2,5mg of enrofloxacin/kg bw/day for 3 day s (equivalent to 2.5 ml of ROXACIN/100 kg bw). This rate may be doubled to 5 mg/kg bw (equival ent to 5 ml of ROXACIN/100kg bw) for 5 days in case of complicated respiratory disease. Administration route: cattle – SC, pigs – IM. Not more than 2.5 ml should be administered at any one intramuscular injection site. Not more than 10 ml should be administered at any one subcutaneous injection site Cattle: E. coli mastitis: Administer by slow intravenous injection 5mg of enrofloxacin/kg bw (equivalent to 5ml of ROXACIN/100kg bw) daily for 2 days. CONTRAINDICATIONS: Do not use for prophylaxis. Do not use when resista nce/cross resistance to (Fluoro)quinolones is known to occur. Do not use in the case of known hyp ersensitivity to fluoroquinolones or to any of the excipients. WITHDRAWAL PERIOD: Cattle: Pigs: Subcutaneous use Intravenous use Intramuscular Use Meat and offal: 10 days Meat and offal: 4 days Meat and offal: 10 days Milk: 84 hours (7 milkings) Milk: 72 hours (6 milki ngs) PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES: Enrofloxacin is bactericidal in action with a conce ntration dependent activity against a wide range of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria and mycopl asmas. The mechanism of action of the quinolones relies upon their ability to inhibit bac terial DNA gyrase, an enzyme responsible for controlling the supercoiling of bacterial DNA durin g replication. The fluoroquinolones also possess activity against bacteria in the stationary phase b y an alteration of the permeability of the outer membrane phospholipid cell wall
Competitor's products
|
|||||||||||||
|
2009-2025 © All Rights Reserved
|